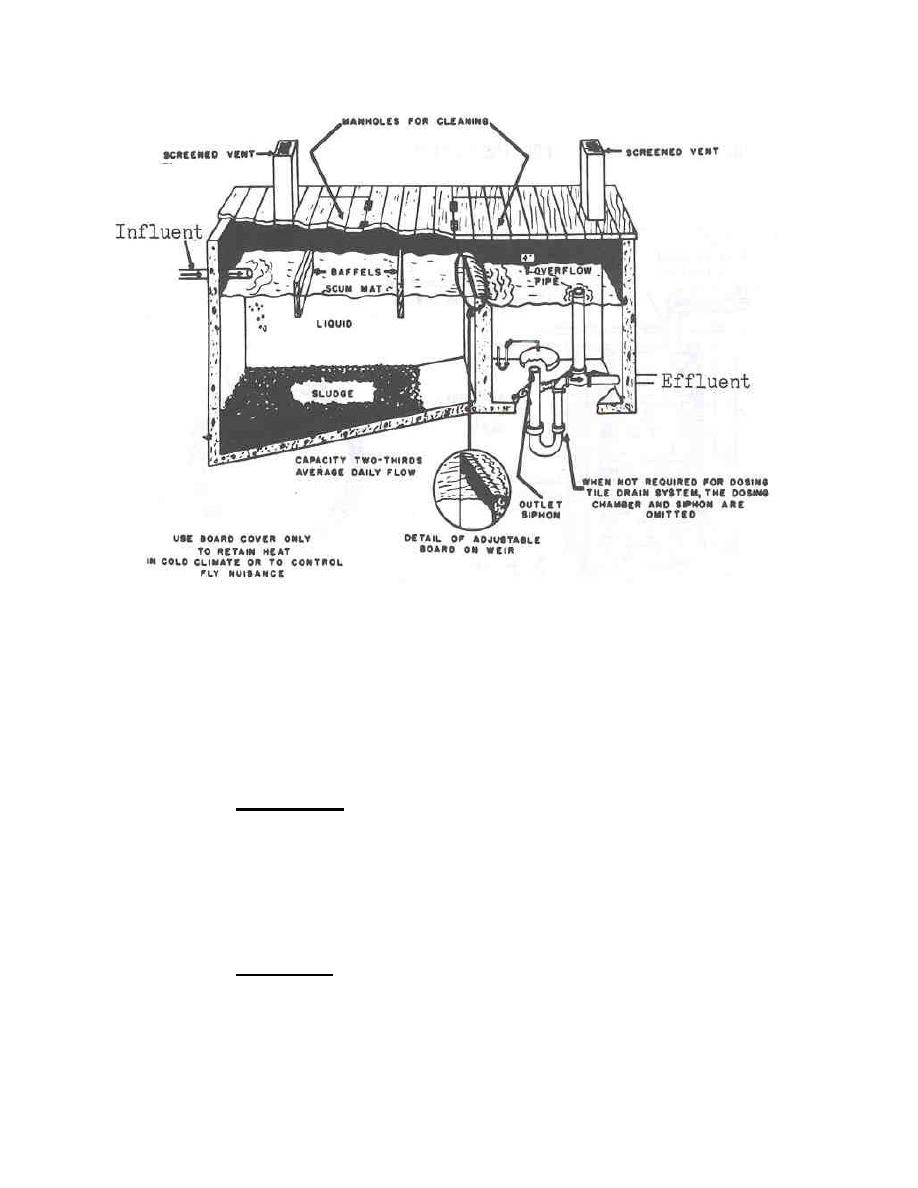
Figure 1-16. Septic tank with dosing tank and automatic siphon.
1-17. ALTERNATE DISPOSAL METHODS
a. Seepage Beds and Seepage Pits. When the available land area is
insufficient to accommodate a complete soil absorption system, but the soil percolation
test indicates an acceptable percolation rate, the following alternatives may be
considered.
(1) Seepage bed. A seepage bed is essentially the same as an absorption
trench except that it consists of a wider trench in which several distribution lines are laid.
Distribution lines are placed 6 feet apart and 3 feet from the bed sidewall. Otherwise,
the construction criteria are the same as for absorption trenches. The same amount of
bottom absorption area is required (see Tables 1-3 and 1-4), but the wide bed makes
more efficient use of land than a series of trenches with wasted land between the
trenches.
(2) Seepage pit. A seepage pit (see Figure 1-17) is a vertical cylindrical pit
constructed of unmortared masonry. The pit is surrounded by 6 inches of rock or gravel
fill on the sides and 12 inches underneath. The entire surface area, both sides and
bottom, is considered absorption area and permits seepage of septic tank effluent for
further percolation through the gravel and surrounding soil. The seepage pit should
MD0161
1-40



 Previous Page
Previous Page
