Section III. EAR INJURIES/DISORDERS
4-8.
GENERAL CONSIDERATIONS
Most ear injuries and disorders are not fatal. Instead, they may cause serious
communication problems. Untreated hearing loss or deafness can impair a person's
ability to interact with others. Additionally, ear disorders can disturb an individual's
equilibrium (balance)
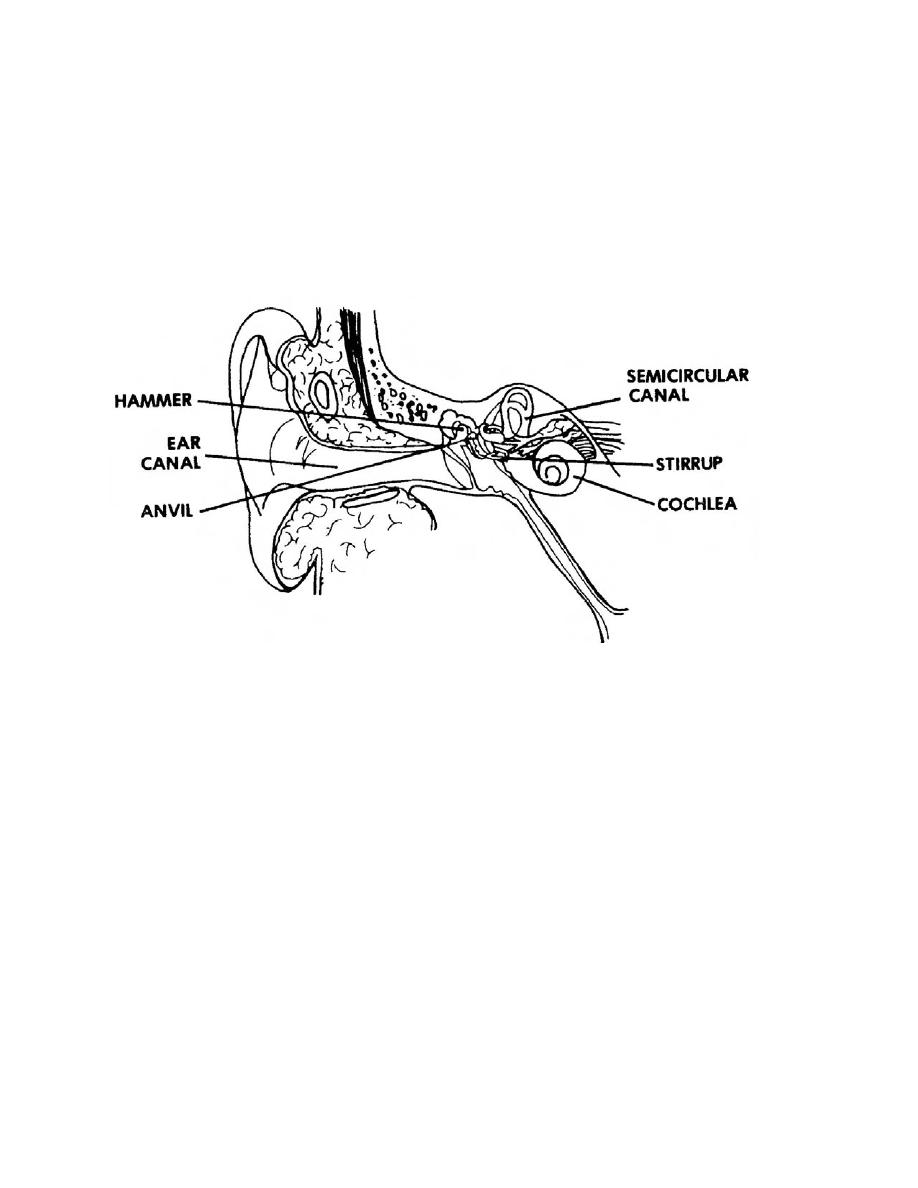
Figure 4-3. Structure of the ear.
4-9.
HEMATOMA OF THE EXTERNAL EAR
a. Description. The external ear is in an exposed position; therefore, external
ear injuries are very common. Hematoma of the external ear, as accumulation of blood
outside the blood vessels, is caused by a blow to the ear by something blunt. The
accumulation of blood interrupts the nutrition to underlying cartilage. Treatment is
essential not only to restore blood supply to the cartilage but also to avoid deforming
and thickening of the ear.
b. Treatment. For an accumulation of blood without swelling, apply cold
compresses to limit the spread of edema and discoloration. Give analgesics for pain. If
the accumulation of blood is large, aspirate (remove the fluid with a 16-gauge or 18-
gauge needle) the hematoma. Apply a pressure dressing and observe the area for
recurrence of the hematoma.
CAUTION:
Failure to provide proper treatment can result in the patient having a
"cauliflower" ear.
MD0582
4-13



 Previous Page
Previous Page
