fragments of the cytoplasm-megakaryocytes that are found in the bone marrow (others
coming from red bone marrow include: promegakarycocytes and megakaryoblasts).
Unstained platelets appear as small hyaline structures with a diameter of approximately
two microns. When stained with Wright's stain, they have a pale blue cytoplasm with a
dark granular center. Platelets are very fragile and live for a period of about 3 to 5 days.
1-4.
LIQUID CONSTITUENTS
a. Plasma. Blood plasma is a clear, yellowish fluid that accounts for about 55
percent of the total volume of the blood. The chemical nature of plasma is very
complex. It consists of 92 percent water, 7 percent proteins (albumin, globulin, and
fibrinogen), carbohydrates (glucose), lipids (fats, lecithin, and cholesterol), dissolved
gases (oxygen, carbon dioxide, and nitrogen), non-protein nitrogenous substances, and
less than 1 percent of inorganic salts. Blood plasma is the fluid portion of the blood
before clotting occurs. Put another way, plasma from which fibrinogen has been
removed is called serum.
b. Serum. Serum is the fluid portion of blood after the clotting process is
complete. Fibrinogen, the precursor of fibrin, is removed from plasma to form the
framework of the blood clot.
Section II. FORMATION OF BLOOD CELLS
1-5.
EMBRYONIC HEMATOPOIESIS
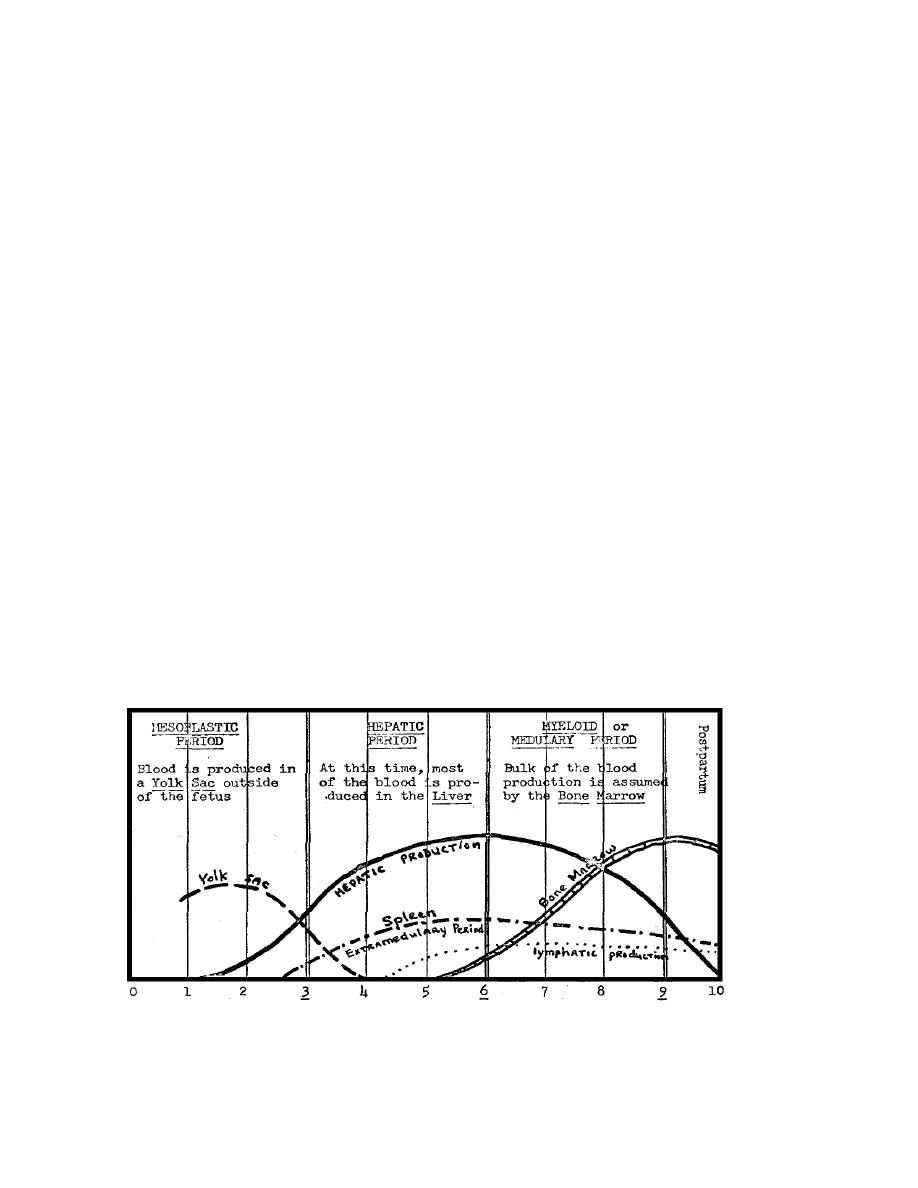
a. The primary source of blood cells is the mesenchyme connective tissue in the
embryo. Three phases of embryonic hematopoiesis merge, resulting in the formation of
blood (see figure 1-2).
b.
Fetal Developmentin months
Figure 1-2. Embryonic hematophoiesis.
MD0853
1-5




 Previous Page
Previous Page
