FRAME 65
Observe that fluid was "drawn" from the cell in
order to achieve equilibrium. Therefore, the cell
was reduced in size. Such an experience is
traumatic for the cell unfortunate enough to be
placed in such a situation. In relation to
intravenous fluids, a hypertonic solution would
cause cell irritation to blood cells and the cells
lining the circulatory system. The patient who is
being administered a hypertonic solution would
experience localized pain in the area of the
administration site. Examples of hypertonic
solutions are most hyperalimentation solutions and
10% dextrose solution.
FRAME 66
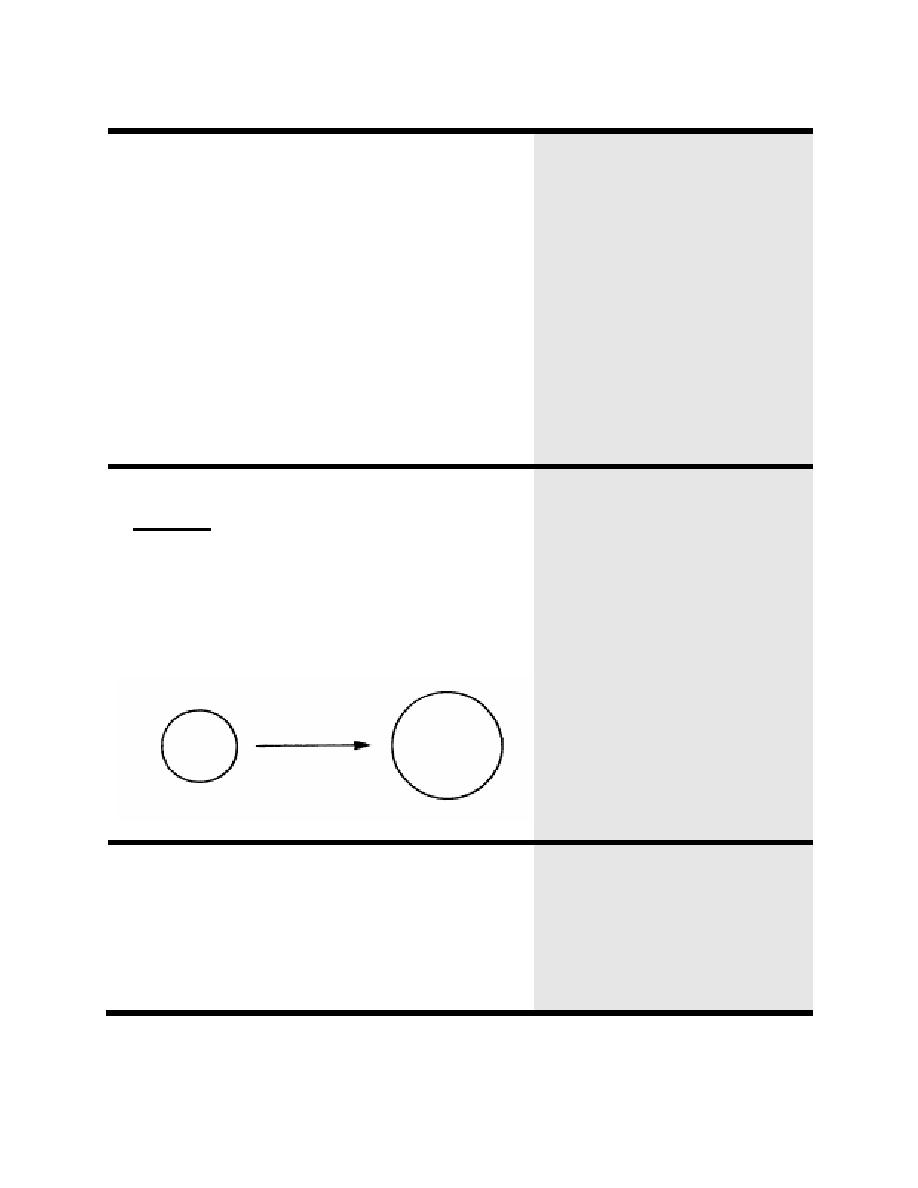
A hypotonic solution is less concentrated than that
of body fluids. That is, the hypotonic solution has
less solute per volume than that of body fluid.
When placed in a hypotonic solution, a cell will
increase in size because water will enter the cell in
an attempt to equalize the concentrations of the cell
and the hypotonic solution:
FRAME 67
As you can see, unfortunate cells exposed to
hypotonic solutions could become irritated and
damage to them could result. Examples of
hypotonic solutions are 0.45% sodium chloride
solution and sterile water for injection.
MD0807
5-22



 Previous Page
Previous Page
