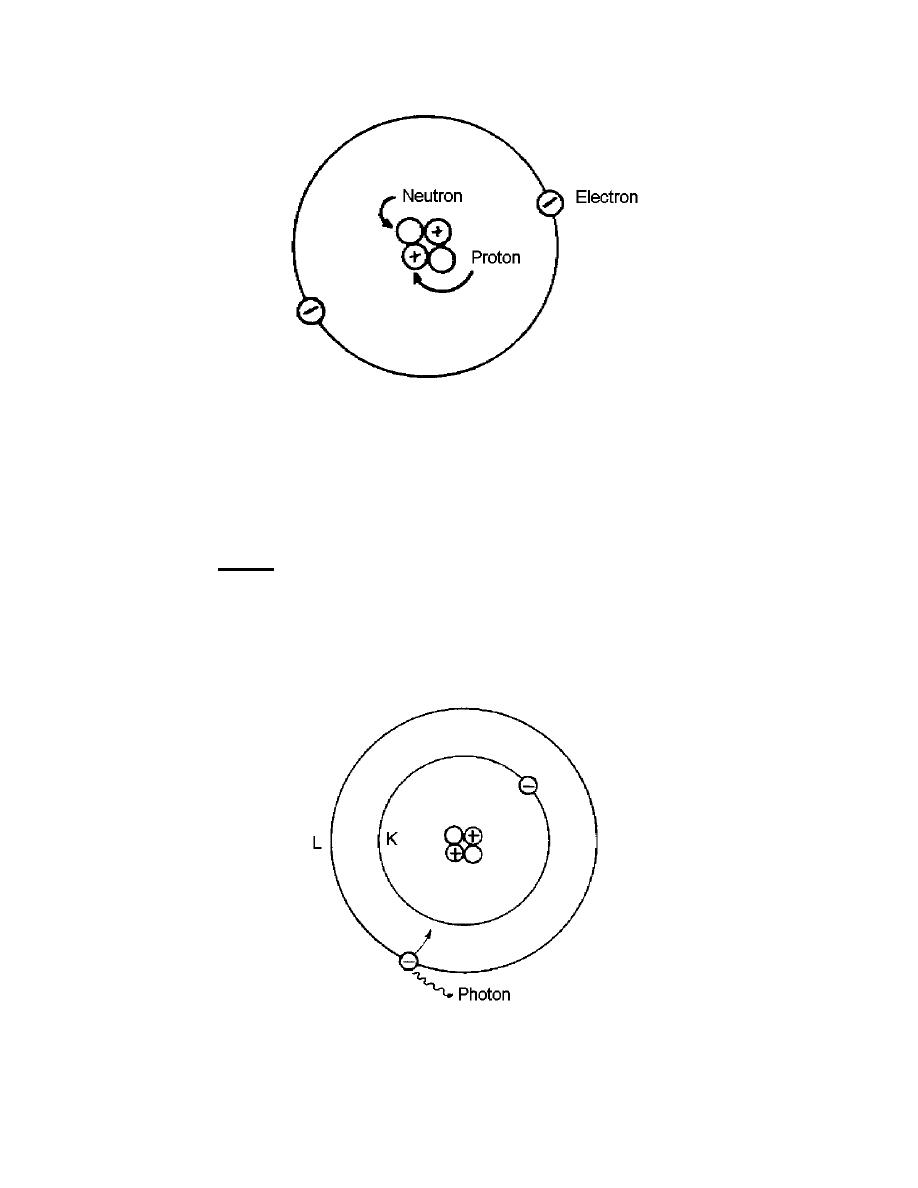
Figure 1-3. Helium atom.
condition is referred to as an "excited" atom. It is caused by subjecting the atom to an
external stimulus, such as a source of radiation or collision with another atomic particle
(Figure 1-4). The electron in the L-shell will jump back into the K-shell and in the
process will give off a bit of electromagnetic energy. For this particular case, there will
be a light of a frequency in the visible range. This bit of electromagnetic energy given
off is called a photon. Therefore, the electronic structure has a great deal to do with the
emission of radiation from matter. One way in which these electron jumps can be
arranged to occur in large numbers is to build a neon lamp. The electric current passing
through the neon gas knocks some of the electrons into higher shells and, in jumping
back, light is given off. Sometimes the jump is referred to as a jump from one energy
level to another.
Figure 1-4. Excited atom.
MD0180
1-7



 Previous Page
Previous Page
